Understanding your customers’ experiences and perceptions is crucial for enhancing your products and services. While quantitative research provides numerical insights, qualitative survey questions dive deeper, exploring the “why” behind customer behaviors.
This article answers what qualitative research questions focus on, their applications, types, and the advantages and disadvantages of using them.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Questions
Surveys can include both qualitative and quantitative questions. Quantitative questions yield numerical data, easily measured and statistically analyzed, like “How many times have you used our app this week?” or “On a scale of 1-10, how satisfied are you with our service?” This data is invaluable for spotting trends, measuring performance, and making data-driven decisions.
Qualitative research questions, however, seek to understand the underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations behind customer actions. They often start with “why,” “how,” or “what.” For instance, “What features do you find most useful in our app?” or “Can you describe a challenge you faced while using our service?”

Our Tip: A Balanced Approach
These qualitative survey questions examples provide richer, more detailed data, invaluable for customer experience (CX) professionals aiming to boost user satisfaction and loyalty. They uncover insights that quantitative data alone can’t, such as emotional responses and personal stories, revealing deeper customer needs and preferences.
A balanced approach, blending qualitative and quantitative research, typically yields the best results. Quantitative data highlights areas needing attention, while qualitative data explains why these issues exist and suggests potential solutions. This combination offers a comprehensive understanding of customer experiences, guiding more effective improvements and innovations.
When Should We Use Qualitative Research Questions?
Qualitative research questions are especially useful in various scenarios. By asking these “why” questions, you uncover insights that shape strategies, conduct market research, and enhance customer experiences.
Exploring Experiences:
Understand how customers interact with your product or service. For instance, “Can you describe your overall experience with our customer support?” This type of question helps you focus on uncovering the nuances of customer interactions, highlighting what works well and what needs improvement.
Investigating Processes:
Gain insights into how customers use your product. For example, “Can you walk us through how you typically use our app?” This helps identify pain points in the user journey and opportunities to streamline processes.
Addressing Sensitive Topics:
Delve into issues that might be uncomfortable or nuanced, such as “How do you feel about the privacy features of our app?” A careful approach ensures respondents feel safe and respected while sharing their thoughts.
Understanding Change:
Comprehend shifts in customer behavior or preferences, like “Why did you decide to upgrade to our premium plan?” Understanding these reasons guides strategic decisions and product development.
Uncovering Motivations:
Discover what drives customer decisions. For instance, “What motivated you to choose our product over competitors?” This helps understand the unique value propositions that attract customers to your brand.
Identifying Expectations:
Determine what customers expect from your service or product. For example, “What features would you like to see in future updates?” Knowing these expectations helps prioritize developments to enhance satisfaction and loyalty.
Evaluating Impact:
Assess the impact of changes or new features. For instance, “How has the new dashboard improved your workflow?” This provides direct feedback on recent updates, helping measure their effectiveness.
Types of Qualitative Research Questions – Examples
There are various types of qualitative research questions, each serving a distinct purpose. Here are some examples focused on customer experience and marketing:
Descriptive
Descriptive questions gather detailed information about specific aspects of your product or service, helping understand what customers notice and appreciate.
Examples:
- “What specific design elements stand out in our app?”
- “What features do you find most helpful on our website?”
- “Which elements of our service do you value most, and why?”
These effective qualitative research questions uncover details often missed in broader surveys. Customers might highlight a feature’s simplicity or the aesthetic appeal of your app’s interface, offering actionable insights for your design team.
Predictive
Predictive questions explore potential future behaviors or outcomes, helping anticipate customer needs and preferences for proactive improvements.
Examples:
- “If we had a project management tool integration for our app, how often would you use it?”
- “How likely are you to recommend our service to a friend after using our new feature?”
- “What impact do you think adding live chat support would have on your overall satisfaction?”
Predictive questions gauge the potential success of new features or changes before implementation, allowing adjustments based on customer feedback and reducing the risk of investing in unwanted developments.
Experiential
Experiential questions focus on understanding customers’ personal experiences and emotions, providing insights into their journey and emotional responses at various touchpoints.
Examples:
- “How would you describe your first impressions of our application?”
- “Can you share a time when our customer service exceeded your expectations?”
- “What emotions do you associate with using our product, and why?”
These questions help qualitative research methods identify emotional factors influencing customer satisfaction and loyalty, amplifying positive experiences and addressing negative ones to enhance overall perception.
Comparative
Comparative questions draw comparisons between different products, services, or experiences, helping understand your competitive position and identify areas for improvement.
Examples:
- “Was the pricing clear and easy to understand compared to our competitors?”
- “How does our product compare to others you’ve used in terms of ease of use?”
- “In what ways do you think our service stands out from competitors?”
Comparative questions reveal strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors, guiding strategies to enhance unique selling points and address gaps in your offerings.
Process-oriented
Process-oriented questions explore the steps customers take when interacting with your product or service, identifying barriers and opportunities to optimize the customer journey.
Examples:
- “What are your next steps when you encounter an issue with our product?”
- “How do you typically find information on our website?”
- “What process do you follow to decide to make a purchase on our platform?”
Each qualitative research question, together with its statistical analysis, provide insights into practical aspects of customer interactions, highlighting areas to streamline and make the UX more intuitive.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Qualitative Questions in Surveys
Qualitative methods in conducting online research have their strengths and weaknesses. Let’s take a brief look at them.
Advantages
In-Depth Data Gathering:
Qualitative questions provide detailed insights into customer thoughts and feelings, helping understand the “why” behind their actions. This depth leads to more targeted and effective improvements.
Encouraging Customers to Speak Their Minds:
These questions invite open-ended responses, letting customers express their opinions and experiences in their own words. This uncovers insights that structured questions might miss, capturing the full range of customer sentiments.
Participant Engagement:
Qualitative questions make surveys more engaging, encouraging participants to spend more time providing thoughtful answers. Engaged participants offer richer data, leading to more valuable insights.
Flexibility in Responses:
Unlike quantitative questions, which limit answers to predefined options, qualitative questions let respondents answer in their own words. This flexibility reveals unexpected insights and nuances.
Contextual Understanding:
Qualitative responses include context that quantitative data lacks, providing a fuller picture of customer experiences and perceptions. This context is crucial for accurately interpreting feedback and making informed decisions.
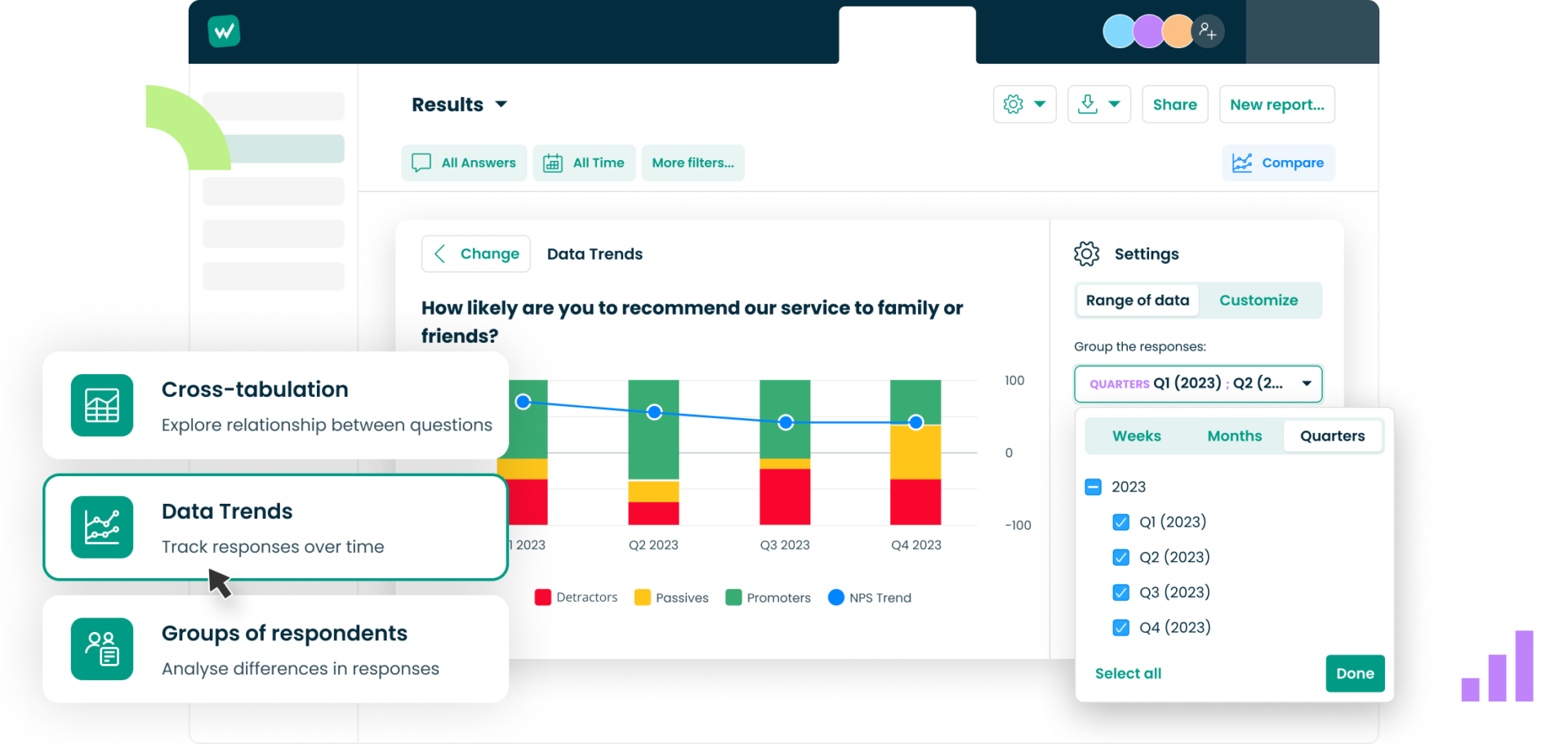
Disadvantages
Sample Bias:
The open-ended nature of qualitative questions may attract responses from customers with strong opinions, potentially skewing the data. Ensure a diverse range of participants to mitigate this bias.
Privacy Issues:
Collecting detailed personal information can raise privacy concerns, requiring careful data handling to ensure confidentiality. Robust data protection measures are essential to maintain customer trust.
Time-Consuming Analysis:
Analyzing qualitative data is time-consuming, requiring a nuanced approach compared to quantitative data. This often involves coding responses, identifying themes, and interpreting meanings, which can be labor-intensive.
Subjectivity in Interpretation:
Qualitative data is inherently subjective, both in how respondents articulate their answers and in how researchers interpret them. Ensuring consistent, unbiased interpretation requires careful methodological rigor.
Limited Generalizability:
Qualitative data is detailed and specific, making it harder to generalize findings across a larger population. While valuable, these insights often need to be complemented with quantitative research to provide a broader perspective.
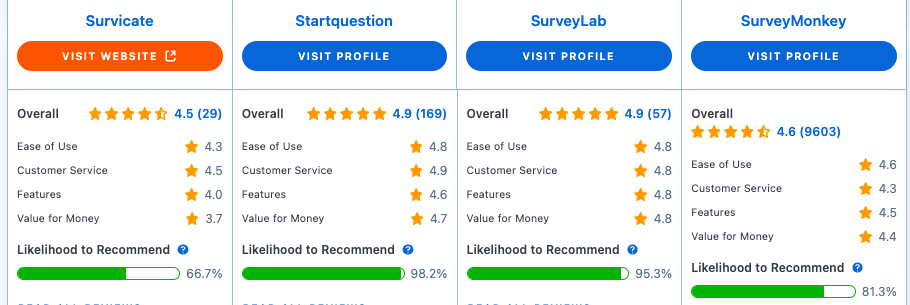
Good Qualitative Research Questions – Sum Up
Incorporating qualitative surveys into your research can unlock valuable insights that quantitative data alone can’t. By crafting and strategically using these questions, CX specialists can gain a deeper understanding of customer experiences, motivations, and preferences. Though challenges exist with qualitative data, its rich, detailed feedback is instrumental in shaping product and service strategies, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Conducting qualitative research explore the nuanced aspects of CX in focus groups, laying the foundation for meaningful improvements. Whether you’re understanding customer behavior, addressing sensitive issues, or evaluating changes’ impact, qualitative questions offer the depth needed for informed decision-making. By balancing these with quantitative measures, you get a comprehensive view of your customers, enabling you to create more personalized, responsive, and effective CX strategies.
Tool For Quantitative and Qualitative Questions
As you choose qualitative research questions for your surveys, consider your research objective and your target audience’s unique contexts. Tailor questions to elicit detailed, thoughtful responses guiding your efforts to boost customer satisfaction and loyalty. Remember, the ultimate aim is to understand and meet your customers’ needs more effectively, fostering stronger relationships and driving long-term business success.
Ready to ask the right qualitative research questions?










