In data analysis, where information can be overwhelming, the advent of Natural Language Processing (NLP) has introduced a breath of fresh air. This field of artificial intelligence and deep learning models focuses on enabling computers to understand and interpret human language, posing an intriguing question: can NLP truly revolutionize survey analysis?
Join us as we explore the intricacies of natural language understanding with massive help from NLP, its widespread applications, and its potential to redefine how we extract insights from answers provided by survey respondents so you will no longer have to waste time on manual analysis.
What Is Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Before moving to deeper insights, let’s start with a brief definition.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in computer science is the ability of artificial intelligence (AI) products and services to understand human speech or written text using statistical methods and machine learning models.
While essential speech-to-text software can convert spoken words to written form, it only scratches the surface of NLP’s capabilities. NLP can capture the context and meaning of complex terminology and phrasing and extract abstract qualities such as sentiment from the survey responses, online reviews or Net Promoter Score results (NPS surveys).

Linguistic Analysis with Neural Network Architectures
Humans can decipher the meaning and intention behind misspelled or indirect language; NLP software can replicate this process.
Artificial intelligence aims to make machines react in a way that resembles human behavior using technology called neural network models. In other words, AI is designed to mimic human-like responses as closely as possible.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) encompasses various applications such as speech recognition, sentiment analysis, machine translation, and chatbots. To perform these tasks, NLP systems often rely on models of artificial neural networks (ANNs), which, as we already know, imitate the structure and function of biological neurons.
Do you also have a headache from too much theory? It’s time to move on to practice, i.e., using modern technology to analyze survey results better.
Using NLP for Open-Ended Survey Questions
In survey design, open-ended questions are gateways to unfiltered and nuanced survey responses.
Unlike closed-ended questions that offer predefined choices, open-ended queries invite respondents to express thoughts, opinions, and experiences in their own words. While this provides a rich tapestry of qualitative data, the challenge lies in effectively unraveling and interpreting these narratives.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology can change the game significantly.

Open Ended Survey Responses in a NLP Survey
A multi-faceted approach is necessary for effectively utilizing open-ended survey responses in Natural Language Processing to extract valuable insights from customer satisfaction and other questionnaires.
Here’s how it works.
Text Preprocessing
Before the analysis begins, NLP engages in text preprocessing. It involves cleaning up the raw text data, known as raw data in the survey world, removing redundant or stop words, and standardizing formats. The result is a refined dataset (structured data) ready for deeper exploration.
Named Entity Recognition (NER)
In the vast expanse of open-ended responses, crucial entities such as names, locations, and organizations often play pivotal roles. NER in NLP identifies and categorizes these entities, enhancing the organization’s ability to discern critical information within the qualitative survey data set.
Topic Modeling
Picture open-ended survey responses as a tapestry of thoughts. Topic modeling within NLP acts as the illuminating thread and content analysis, grouping unstructured text into related ideas and thoughts. It simplifies the analysis process and unveils prevalent themes that might have gone unnoticed in unstructured data.
Examples of Open-Ended Survey Questions
Now, let’s look at some examples of questions that often appear in HR, CX, or market research surveys. Let’s see how, with the help of NLP and language modeling tasks, you can extract valuable essence from respondents’ answers to open-ended questions.
Product/Customer Feedback:
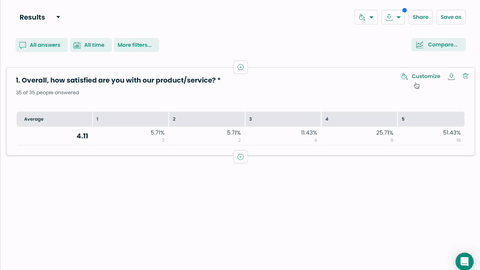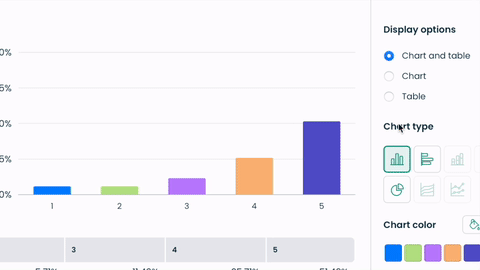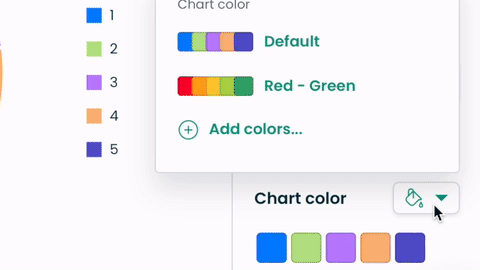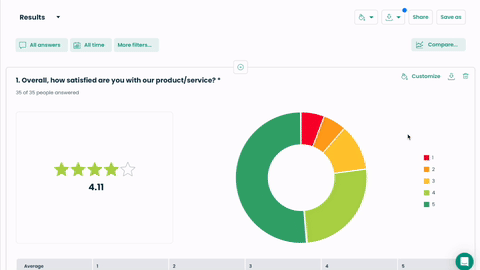
“On a scale of 1 to 5, how satisfied are you with our product?”
“Please share your thoughts on your experience with our product.”
NLP Application:
Analyzing sentiments expressed and identifying key phrases to understand specific aspects that contribute to satisfaction or dissatisfaction.

Employee Engagement:
“Are you satisfied with the current work environment? (Yes/No)”
“How would you describe the work environment and what improvements would you suggest?”
NLP Application:
Extracting recurring themes and sentiments to gain a deeper understanding of the factors influencing employee satisfaction.
Market Research:
“Which of the following features is most important to you?”
“Is there anything else you would like to share regarding your preferences for product features?”
NLP Application:
Identifying emerging trends or unanticipated preferences expressed by respondents that might not be covered by predefined choices.
Using NLP and deep neural networks in open-ended survey questions has many benefits.
It not only allows us to interpret text and convert qualitative responses into valuable insights, but it also enables technology to mimic the cognitive processes our minds naturally use to comprehend language.
By embracing these advanced techniques, we can unlock the full potential of open-ended survey questions and gain a deeper understanding of the responses we receive.
Most Popular Natural Language Processing Use Cases
It is time to see how the fusion of computer programming and machine learning techniques, like training data, endeavors to decipher and harness extensive textual data.
Within the expansive landscape of Natural Language Processing lies many possibilities for scrutinizing your open-ended survey responses. However, navigating this multitude of applications and selecting the most effective one can take time and effort.
In the following sections, we will guide you through three of the most sought-after applications within NLP, unraveling their potential and simplifying your exploration of this dynamic field.
The Word Cloud (Keyword Extraction)
Using NLP-powered word clouds, visualizing data has become more captivating than ever. Imagine a graphic representation of keywords extracted from survey responses, forming clusters of words or terms highlighting the prevalent themes. It simplifies the identification of critical topics and adds a visually engaging layer to the data analysis process.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is a tool that enables computers to identify the emotional tone present in written text. It goes beyond simply counting positive or negative sentiments, diving into the subtleties to provide qualitative depth to quantitative data. When applied to survey responses, organizations can gain insight into the emotional nuances of their audience, taking survey analysis to a new level of understanding.
Contextual Understanding
Natural Language Processing (NLP) can understand the context in which words are used, going beyond literal interpretation. In survey analysis, this means understanding the reasons behind opinions or suggestions rather than just the words themselves. It adds a layer of depth that traditional analysis may need to capture.
How TF-IDF Works
TF-IDF is another important concept in Natural Language Processing we’d like to cover in this article. Don’t be fooled by the name. It is not a forgotten Star Wars hero or a keyboard shortcut but a technique that can help analyze survey responses. Here’s how it works.
TF-IDF in Survey Results & Text Analysis
TF-IDF is a powerful tool for analyzing survey data. It measures the uniqueness of words across the entire dataset using Term Frequency (TF) and Inverse Document Frequency (IDF). To calculate TF-IDF, multiply TF by IDF to represent a term’s importance numerically. The formula highlights critical insights that might have been overlooked otherwise.
Example to Illustrate the Application of TF-IDF
Imagine conducting a survey on travel preferences, specifically asking respondents about their dream destinations and reasons for choosing them. TF-IDF comes into play, spotlighting unique expressions that reveal underlying themes within the responses.
Common Phrases with High TF-IDF:
If numerous respondents mention terms like “cultural immersion” and “local cuisine” when describing their ideal travel experiences, TF-IDF assigns a high score to these terms. These expressions become the focal points of analysis, indicating a shared emphasis on cultural exploration and gastronomic adventures among respondents.
Distinctive Preferences with High TF-IDF:
On the other hand, TF-IDF might identify less common terms like “off-the-beaten-path destinations” and “adventurous activities.” Despite being mentioned by a smaller subset of respondents, these expressions receive high TF-IDF ratings, signaling their uniqueness and importance within the dataset. Analysts can now delve deeper into these preferences that set a specific group apart.
In this scenario, TF-IDF acts as a guide, not only highlighting commonly shared sentiments but also bringing attention to less frequent yet distinctive expressions. Whether it’s the allure of cultural experiences or the desire for offbeat adventures, TF-IDF ensures that your analysis captures the richness and diversity of responses, allowing unique perspectives to shine through.
When to Use TF-IDF for Survey Analysis
By zooming in on unique expressions and spotlighting key themes, we can uncover the rich diversity of perspectives and insights that make up our world.
Through this process, we can better understand the topics we explore and the people who share their experiences with us. Furthermore, we can prioritize essential elements by facilitating relevant comparisons and making informed decisions that drive meaningful change.
NLP Survey Analysis – Sum Up
It’s fascinating to see how technology can understand the complexity of natural language processing techniques and help us communicate with machines more naturally.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a revolutionary tool that has transformed the field of survey analysis. By combining artificial intelligence and human language, NLP simplifies the analytical process and enhances our understanding of survey responses.
With the advent of NLP, we have embarked on a new journey of survey analysis that is not just about processing data but uncovering the stories behind the responses.
The collaboration between technology and human intelligence is reshaping the landscape of survey analysis, resulting in a more nuanced, insightful, and efficient approach to extracting meaning from the voices of survey participants.
We are at the forefront of this new era of survey analysis, where the fusion of technology and human intelligence unlocks a wealth of previously hidden knowledge in plain sight. Let us continue to embrace NLP’s capabilities and explore its endless possibilities.
Ready to bring your survey analysis to the next level?




