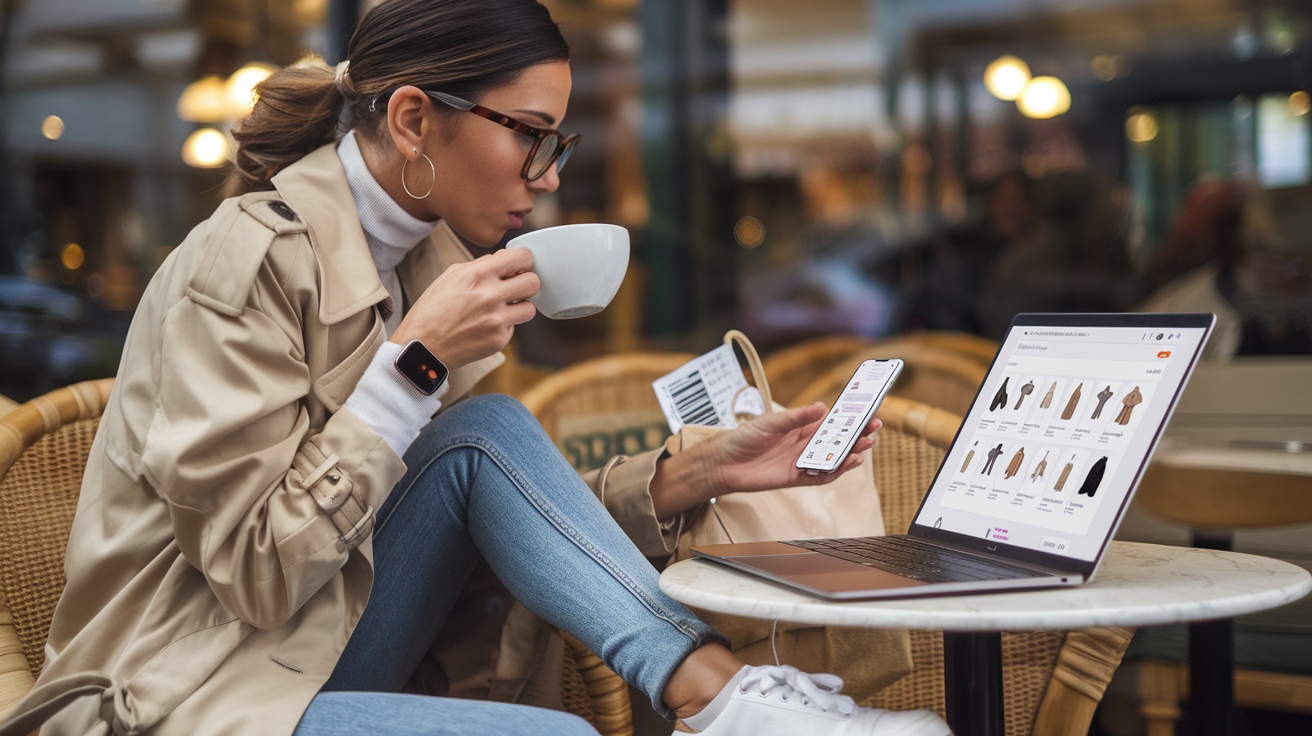
Imagine this: a customer starts their journey scrolling through Instagram, eyeing a sleek new jacket from their favorite brand. With a single tap, they’re on the brand’s website, adding it to their cart. But instead of checking out, they visit the store to see it in person. The next day, they receive a personalized email reminding them about the jacket, with an exclusive offer for in-store pickup. It isn’t the future of retail—it’s the power of omnichannel.
In the age of customer-centric commerce, brands must master the art of delivering a unified journey across multiple touchpoints. Welcome to the world of omnichannel retail, where seamless transitions between channels make the customer experience effortless, engaging, and personalized.
How Does Omnichannel Work?
Let’s start with a brief definition.
Omnichannel in customer experience is a strategy that integrates multiple communication channels—both digital and physical—into a unified experience. This concept ensures that customers can interact with a brand through various touchpoints (e.g., websites, mobile apps, social media, in-store, or customer service) without friction, maintaining a consistent experience across all channels.
Omnichannel Customer Interactions in Practice
We’ll illustrate how an omnichannel experience works in retail.
- Research Phase
Meet John. John is looking for a new laptop. He visits a retail brand’s website from his desktop computer, browsing through various models, adding a couple of options to his wishlist. He logs into his account but decides to continue his research later.
- Mobile Engagement
The next day, John is on his lunch break and opens the brand’s mobile app. He finds his saved wishlist synced automatically. This consistency in the experience allows him to pick up where he left off. He reads reviews, compares prices, and watches a video demo—all from the app. He uses the app’s live chat feature to ask a customer service representative a question about the laptop’s battery life. The rep has access to John’s browsing history and wishlist, so they can provide personalized customer experience and recommendations.
- In-Store Visit
John decides to check out one of the laptops in person. He visits the brand’s store. As he walks in, an in-store associate pulls up his purchase history and wishlist on their tablet, since it’s linked to John’s online account. John sees the exact models he was considering, and the associate provides him with details, including promotions or stock availability.
- Purchase (Multiple-Channels)
After trying the laptop in-store, John isn’t ready to make an immediate purchase, so he leaves. A few days later, while at home, he receives an email from the brand offering a personalized discount on one of the laptops he viewed. He clicks through the email, finalizes the purchase on the brand’s website, and opts for in-store pickup.
- Post-Purchase Experience
After receiving the laptop, John experiences an issue with the setup. He contacts customer support via phone. The support representative already has his order history and product information on hand, so John doesn’t have to repeat any details. The next day, John receives a satisfaction survey asking about consistent customer experience with the purchase and service, completing the omnichannel loop.
Try Ready-To-Use CX Surveys
Here you will find more customer experience survey templates.
Omnichannel vs. Multichannel Experience
We owe you a definition of multichannel.
Multichannel Strategy [Definition]
A multichannel experience means that a brand offers multiple ways for customers to interact with it, such as through its website, mobile app, social media, physical store, or customer service. However, each of these channels operates independently—they may not share data or be connected in any meaningful way. The customer is forced to engage in separate interactions depending on the channel.
Omnichannel and Multichannel Strategies – Key Differences
Here’s a detailed comparison to illustrate the key distinctions between both approaches.
Data Integration
- Multichannel:
In a multichannel marketing setup, customer data is often kept separate within each channel, creating disconnected customer experiences.
- Omnichannel:
Omnichannel systems share customer data across all channels, allowing store associates to access browsing history and enrich customer profiles for personalized interactions.
Customer Journey
- Multichannel:
Customers engage separately with online and offline channels, such as receiving a marketing email, visiting a store, and using a mobile app. However, these experiences are disconnected, leading to disjointed and frustrating journeys.
- Omnichannel:
The customer journey should be seamless across all channels. For example, items added to the cart on a desktop should be accessible on the mobile app and visible to store associates in a physical store. It allows for a smooth transition between channels without losing progress.
Consistency of Experience
- Multichannel:
Experiences can differ across channels, with varying tones, messaging, and offers. Each channel operates independently, leading to inconsistencies in the brand’s presentation.
- Omnichannel:
The customer experience is consistent across all channels, providing a unified approach to messaging, branding, promotions, and customer service. This omnichannel marketing strategy reinforces customer relationships and brand identity at every touchpoint.
Channel Switching
- Multichannel:
Switching between channels in a multichannel approach can be a pain point for customers, as they may have to re-enter information or redo searches when moving from website to app or online shopping to in-store.
- Omnichannel:
Switching from one or more than one channel to another. In an omnichannel experience, customers can seamlessly transition between different touchpoints, such as starting online, moving in-store, and completing a purchase via a mobile app or customer service while preserving all context and data.
Business Focus
- Multichannel:
Multichannel retail strategy focuses on maximizing individual channel performance. It can lead to separate objectives and independent departmental work.
- Omnichannel:
Omnichannel aims to optimize the entire customer journey by integrating all marketing channels to offer a seamless and unified experience. It requires increased collaboration across departments to ensure a cohesive journey across all touchpoints.
Customer Expectations
- Multichannel:
Customers with multichannel interactions often have lower expectations for channel integration. They anticipate good service on each channel individually but understand the potential need to repeat information or restart their journey when switching between channels.
- Omnichannel:
Today’s customers expect seamless omnichannel experiences where their data, preferences, and history carry over across all channels. Brands must provide personalized, consistent service at every touchpoint.

Five Benefits of Omnichannel
Though we tend to subconsciously believe that omnichannel is the best approach to business and marketing efforts in the 21st century, let’s examine the hard evidence and learn about its advantages.
Builds Customer Loyalty
Omnichannel marketing boosts customer loyalty by providing a consistent and personalized experience across all channels. Sephora uses omnichannel to track online purchases and store visits. Customers can use the app to scan products, view purchase history, and get personalized recommendations, building strong loyalty.
Enhances Customer Service
Omnichannel streamlines business customer service by providing comprehensive customer data across all touchpoints, enabling faster and more accurate solutions. The support team in Amazon accesses complete purchase history to quickly resolve customer issues across chat, email, or phone.
Increases Brand Recognition
Companies like Nike maintain brand recognition by ensuring a consistent customer experience across all platforms, unifying the brand voice, design elements, and product recommendations. These strategies maintain consistent branding and messaging across all customer touchpoints, reinforcing brand identity for easier recognition and recall.
Helps Visualise Customer Journey Better
With an omnichannel approach, businesses can track how customers move between channels, identify effective touchpoints, and improve strategies to enhance the overall experience. Disney can track guest interactions across mobile apps, websites, and in-park kiosks to identify trends and make data-driven decisions for improvements.
Saves Time and Money
Omnichannel strategies save time and costs for businesses and customers by streamlining systems and processes. Starbucks has enhanced its customer journey by integrating its loyalty program across its app, website, and physical stores. This integration reduces wait times, improves efficiency, and saves time and money for both the brand and customers.
Omnichannel Commerce: How Does It Help in Retail?
Here are some examples of how real businesses use an omnichannel to their advantage:
Connecting Digital and Physical Experiences
Omnichannel retailing connects online and in-store shopping, providing consistent data, promotions, and personalized customer experiences. It enhances satisfaction and drives more foot traffic through the click-and-collect option.
- Key Features of This Strategy:
App Integration: Customers can browse products online, add them to their cart or wish list, and access the same information in-store through the app. The app also provides personalized recommendations based on past purchases and preferences.
In-Store Digital Services: Stores are equipped with digital experiences, such as self-service kiosks where customers can scan products for more information, see reviews, and check for different sizes and colors.
Click-and-Collect: Customers can buy products online and pick them up in-store, often within the same day, with notifications sent through the app when the order is ready.
Personalized Omnichannel Shopping
Retailers focusing on personalization create omnichannel strategies integrating loyalty programs, mobile apps, and in-store digital tools to deliver a highly personalized shopping experience, leading to enhanced loyalty and conversion rates.
- Key Features of This Strategy:
App & Loyalty Program Integration: Mobile apps are fully integrated with loyalty programs, allowing customers to track purchases, receive personalized product recommendations, and access special promotions both online and in-store.
In-Store Digital Tools: Stores are equipped with interactive tools that help customers make personalized choices, with the data stored in the app for future use. This ensures customers can revisit their preferences online or in-store.
Seamless Product Information: Customers can check the availability of products in nearby stores using the app or website, making it easy to decide whether to purchase online or visit a store. The system syncs inventory data, ensuring accuracy and dedicated marketing channel.
Cross-Channel Shopping Flexibility
A successful strategy involves offering multiple fulfillment options and creating a seamless connection between digital and physical assets to improve customer satisfaction and drive increased sales.
- Key Features of This Strategy:
Same-Day Services: Offering services like Drive Up, where customers order online and pick up items from their car at a nearby store, provides convenience. Similarly, Order Pickup allows customers to collect orders from designated in-store locations.
Delivery Service Integration: Some brands integrate with third-party delivery services to offer same-day delivery for many products, enhancing the customer experience with faster options.
App-Driven Shopping: Apps play a critical role in omnichannel retail, allowing users to browse products, check in-store availability, receive personalized promotions, and even scan items for additional information while shopping in-store.
How Do I Create an Effective Omnichannel Strategy?
Developing an effective omnichannel strategy requires understanding customer behavior and seamlessly integrating touchpoints. It involves five essential steps for building a successful omnichannel approach, focusing on customer journey mapping and data integration.
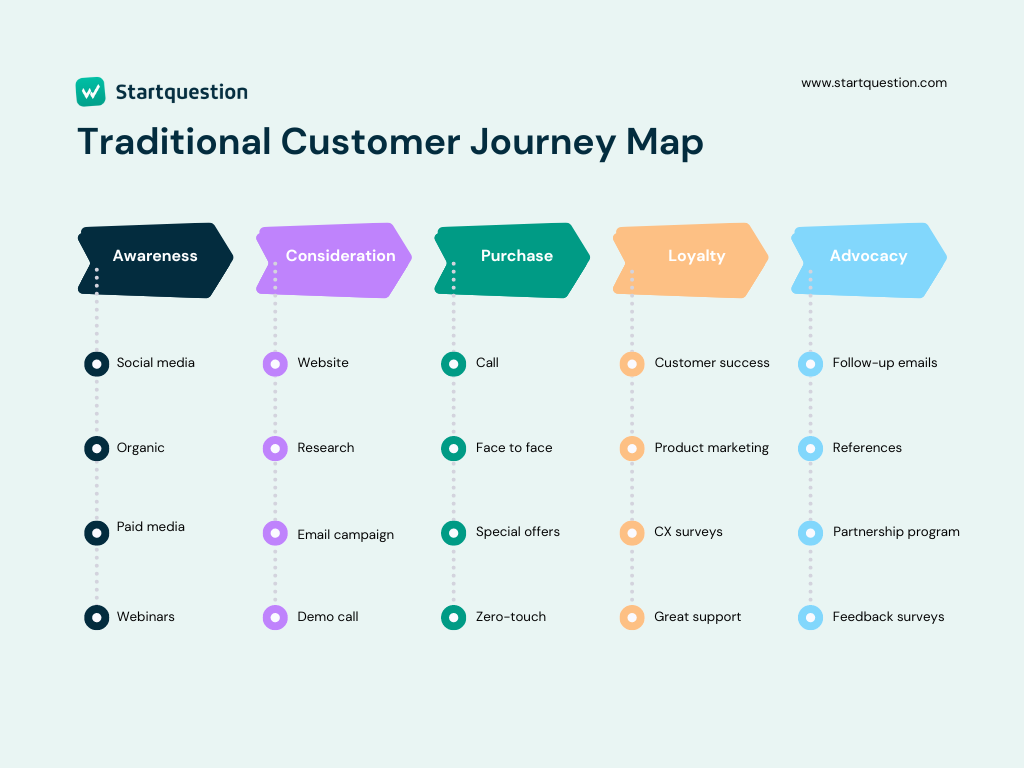
1. Understand and Map the Customer Journey
To create an effective omnichannel strategy, understand customer interactions across all channels through customer journey mapping for smooth touchpoint transitions.
How to Do It:
Collect Data: Analyze customer data to track behaviors across channels like websites, mobile apps, social media, and physical stores.
Identify Key Touchpoints: List the channels where customers interact with your brand and define customer personas to understand their needs and pain points.
Create Journey Maps: Develop maps for each persona, highlighting all touchpoints and ensuring journeys are seamless from start to finish.
Example:
A retail customer might discover a product on social media, visit the website for more details, purchase via a mobile app, and then pick it up in-store. Afterward, a follow-up email encourages them to leave a review, providing opportunities for further engagement.
2. Ensure Data Integration Across Channels
To deliver consistent experiences, data from all channels should be shared and accessible across departments. Customers expect continuity when switching between platforms.
How to Do It:
Centralize Customer Data: Implement a CRM system that gathers data from all touchpoints.
Integrate Systems: Sync online and in-store systems, ensuring a unified view of customer behavior.
Real-Time Data Access: Ensure teams have real-time access to customer data for personalized service and recommendations.
Example:
A seamless integration of mobile apps, loyalty programs, and in-store experiences ensures that customers receive personalized recommendations and consistent interactions across all channels.
3. Align Marketing, Sales, and Customer Service
Success in omnichannel retail requires consistent messaging and coordinated efforts across all departments.
How to Do It:
Unified Messaging: Develop consistent messaging across all channels.
Cross-Department Collaboration: Share customer data between teams to ensure each interaction builds on the previous one.
Integrated Campaigns: Run omnichannel marketing campaigns that guide customers across touchpoints, from emails to in-store experiences.
Example:
Retailers often run email campaigns targeting customers who abandon online shopping carts, offering personalized in-store discounts when they visit a physical location, driving cross-channel engagement.
4. Optimize for Mobile and In-Store Integration
With mobile being a primary tool for shopping, optimizing the mobile experience and connecting it to in-store visits enhances convenience and drives engagement.
How to Do It:
Mobile-First Design: Ensure your website and apps are mobile-responsive for smooth on-the-go browsing and purchasing.
App Features: Develop app features like loyalty program integration, product recommendations, and in-store support such as “scan-and-buy.”
In-Store Mobile Services: Implement mobile payment options and use QR codes to link in-store experiences with digital platforms.
Example:
Customers can check product availability in-store through an app, order via mobile, and then pick up the product in person—seamlessly blending digital and physical shopping experiences.
5. Measure, Refine, and Evolve the Omnichannel Experience
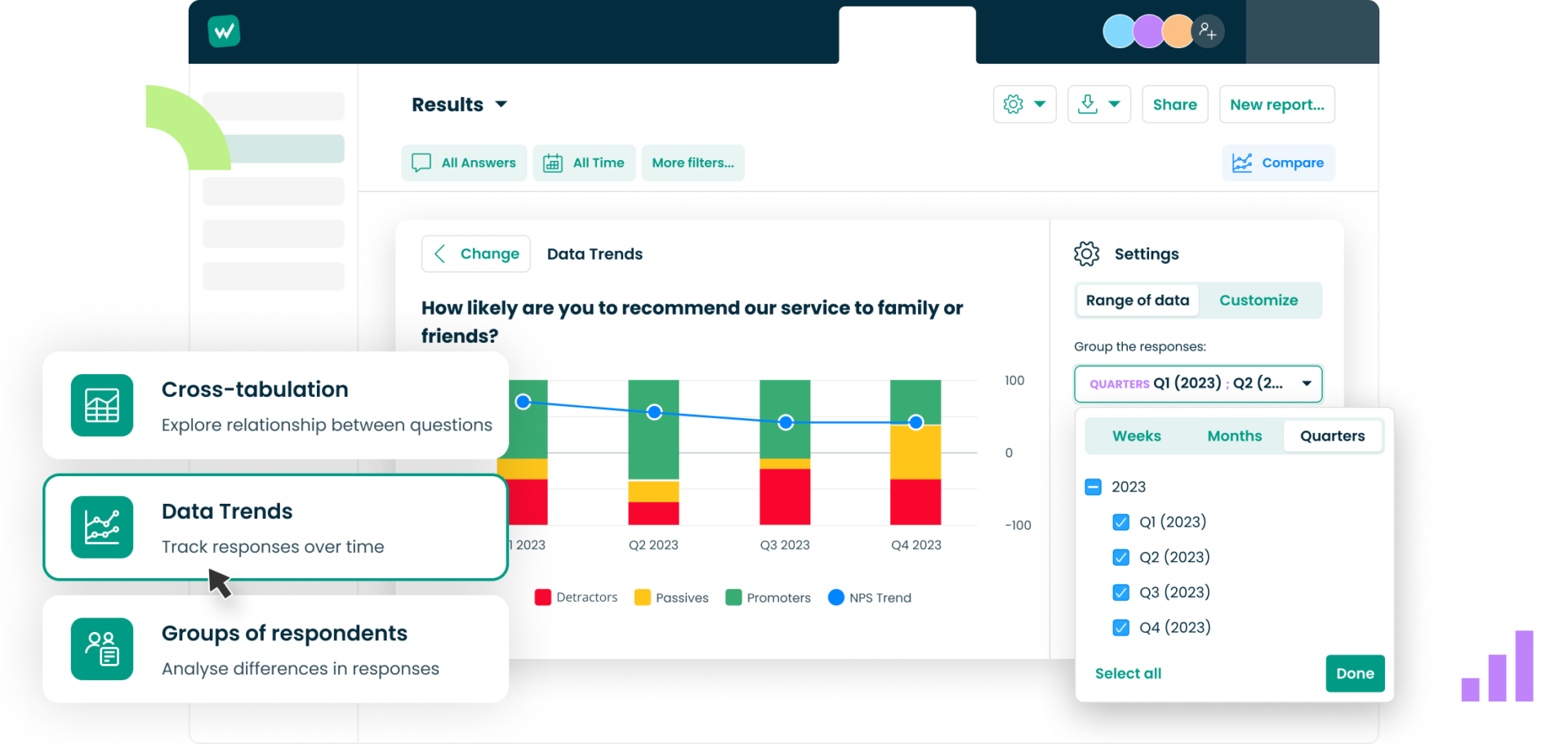
An omnichannel strategy should evolve based on data and feedback, ensuring continuous improvement in the customer experience.
How to Do It:
Monitor Metrics: Track customer satisfaction through surveys and KPIs like conversion rates and customer lifetime value.
A/B Testing: Test different elements of your omnichannel strategy, such as email content or in-store promotions.
Customer Feedback: Regularly collect feedback to identify and address pain points.
Example:
Gathering feedback through surveys and measuring customer engagement with Net Promoter Score helps businesses identify customer journey gaps. Adapting strategies like testing new delivery methods or improving app experiences keeps companies ahead in a competitive market.
Collect Feedback Effortlessly With the CX Survey Tool
To build lasting connections, engaging customers through omnichannel strategies is essential. Seamlessly guiding them across various channels is key to future success. By listening to your customers, you can better understand their needs and make informed business decisions.
Need help in this area? You’re in the right place. Schedule a free demo with our consultant and discover how Startquestion can help you collect customer feedback more efficiently.
Let’s Discuss Your Project & Explore How We Can Assist You
Do you already know how to work with the CX feedback tool?








